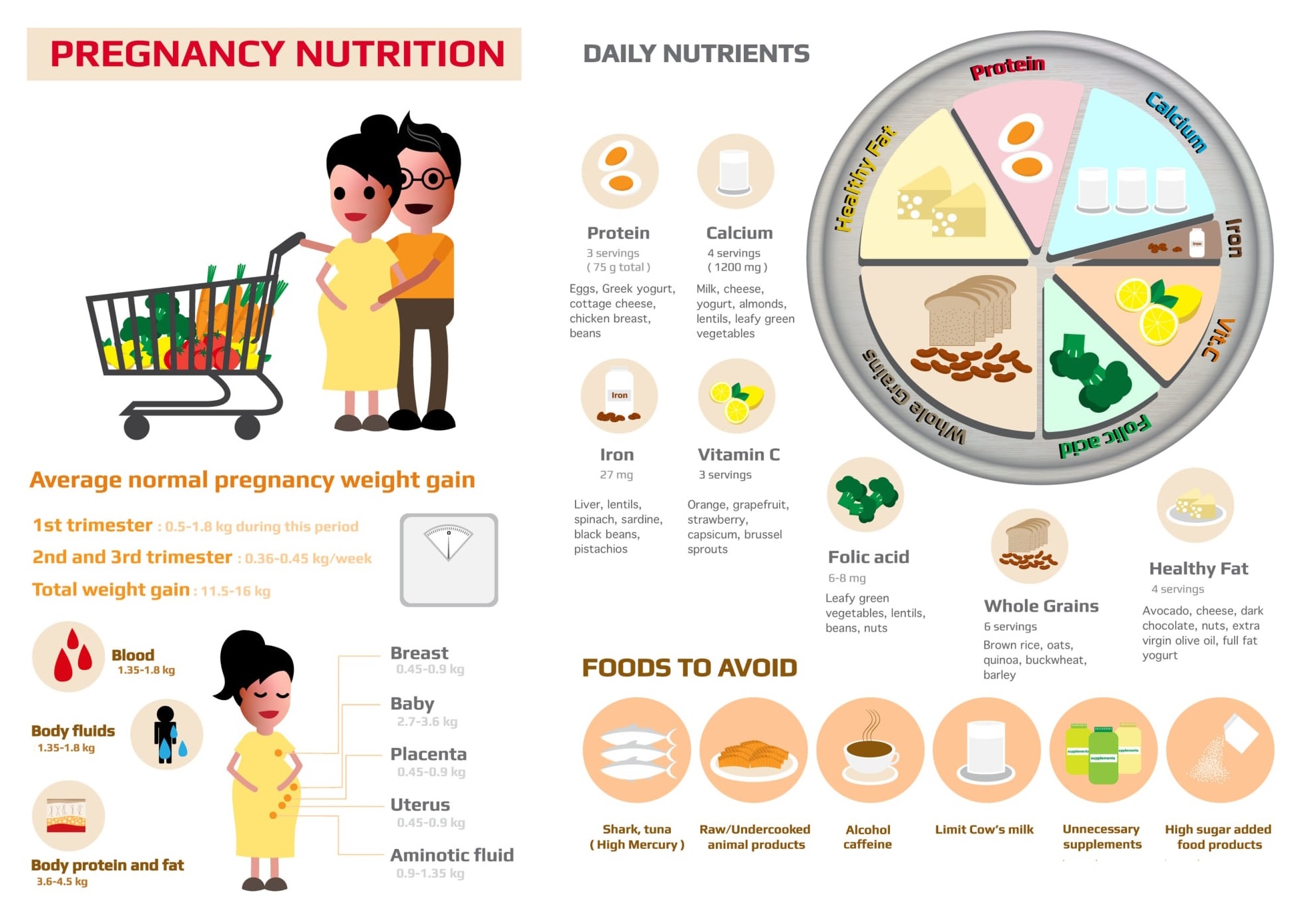
Daily nutrient during pregnancy
Calcium, iron, folic acid, protein, healthy fats, whole grains, and vitamin C are the 7 essential daily nutrients for women during pregnancy.
Calcium
Developing baby needs calcium to build healthy bones and teeth. Calcium also helps a baby grow a healthy heart. Vitamin D will also be required as it aids the absorption of calcium from the stomach.
Food that is rich in calcium included salmon, broccoli, kale, and yogurt.
Iron
Iron is essential to make hemoglobin in the red blood cell. During pregnancy, the amount of blood in your body increases by about 50% to meet the needs of the healthy development of the growing baby.
Getting too little iron during pregnancy can lead to anemia, a common problem during pregnancy which can result in fatigue and an increased risk of infections.
Red meat is rich in iron.
Vitamin C
Pregnant women will need 85mg of vitamin C. However, pregnant women are advised not to take vitamin C supplement, there is concern that taking vitamin C supplement may increase the risk of preterm birth.
Fruits, especially citrus fruit, are especially high in vitamin C, but leafy greens and many other fruits and vegetables are also excellent sources. Choose fresh foods as your source of vitamin C because heat can destroy this vitamin.
Folic acid
Folic acid is also known as folate. It is a B vitamin that is crucial in helping to prevent birth defects in the baby's brain and spine which is also known as neural tube defects.
Most gynecologists recommend that pregnant women take a daily vitamin supplement containing 600 micrograms of folic acid, an amount commonly found in a regular prenatal vitamin.
Food that is rich in folic acid includes leafy green vegetables, fortified or enriched cereals, bread, and pasta.
Protein
More protein is needed during pregnancy. Protein is the building blocks of our body's cell. It is especially important to have enough protein in second and third trimester as the baby is growing faster during these periods.
Food that is rich in protein includes meat, poultry, fish, dried beans and peas, eggs, nuts, tofu.
Whole Grain
Whole grains supply key nutrients such as B vitamins, which are essential for fetal development.
Fibers from whole grains can help to prevent constipation during pregnancy.
Healthy fat
Not all fats are bad. Eating certain fatty foods while pregnant can actually be vital to your growing baby as the right kinds help to fuel proper brain growth and eye development, particularly during the third trimester.
Food source of healthy fats includes nuts like almond, walnut, and fish like salmon.
Food to avoid during pregnancy
According to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, the female immune system weakens during pregnancy. This makes pregnant women more susceptible to bacteria, viruses, and parasites that cause foodborne illnesses.
Undercooked or Raw Fish
First and foremost, do not eat any undercooked or raw fish as they may contain parasites or bacteria.
Secondly, avoid fishes that contains a high level of mercury such as king mackerel, marlin, orange roughy, shark, swordfish, tilefish, and tuna. Mercury consumed during pregnancy has been linked to developmental delays and brain damage in the baby.
Low-mercury fishes, such as salmon, shrimp, pollock, tilapia, or trout are safe to eat, but they should be cooked thoroughly.
Shellfish
It is best to avoid raw shellfish during pregnancy. Raw shellfish like clam, scallop, and oyster contain Vibrio bacteria.
Smoked Seafood
Refrigerated and smoked seafood should be avoided because it could be contaminated with listeria. However, they are safe to eat when they are in an ingredient in a meal that has been cooked, like a casserole.
This type of smoked seafood is often found in the deli section of your grocery store. Canned or shelf-safe smoked seafood is usually fine to eat.
Uncooked Meat
Uncooked seafood and rare or undercooked beef or poultry should be avoided during pregnancy because of the risk of contamination with coliform bacteria, toxoplasmosis, and salmonella.
Soft Cheese
Do not eat soft cheese made from unpasteurized milk. This includes Brie, Feta, Camembert and Roquefort.
Cheese made from unpasteurized milk may contain the virus E.coli or Listeria.
You can instead eat hard cheeses such as cheddar and also make sure that the cheese is made from pasteurized milk.
Unpasteurized Milk
Unpasteurized milk may contain bacteria such as Campylobacter, E. coli, Listeria, or Salmonella.
Juice
Pregnant women should also not drink unpasteurized juice or cider (including freshly squeezed ones) as they may contain E. coli virus.
Egg
Pregnant women should avoid unpasteurized or undercooked eggs as they may contain Salmonella.
Pregnant women should only consume eggs with yolks that are cooked until firm. Cook casseroles and other dishes containing eggs or egg products to 72 degree Celsius.
Vegetable
Raw or undercooked sprouts, such as alfalfa, clover, mung bean, and radish may contain E. coli or Salmonella.
Vegetables are safe and a necessary part of a balanced diet. However, it is essential to ensure that they are washed properly to avoid potential exposure to toxoplasmosis. Toxoplasmosis may be caused by contamination in the soil where the vegetables were grown.Caffeine
Coffee, tea, chocolate and some soft drinks have a high level of caffeine. Pregnant women should limit their consumption to one or two cups in a day.
This is because the caffeine can be passed to the growing fetus very quickly. Furthermore, the unborn baby does not have the enzyme to metabolize the caffeine, causing the caffeine level to build up.
According to one study published by the National Institute of Health, high maternal caffeine intake during pregnancy is associated with the risk of low birth weight in babies.
Alcohol
Pregnant women should stay away from alcohol as it increases the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. Many studies have confirmed that even a small amount can negatively impact the brain development of your baby.
Average pregnancy weight gain
While it is not necessary to keep to these guidelines strictly, it is recommended that for women who were underweight before pregnancy (BMI < 18.5), you should aim to gain an average of 0.5 to 2kg during the first trimester, and 0.4 to 0.6kg per week during the second and third trimesters.
For women who had a normal weight before pregnancy (BMI 18.5-24.9), you should aim to gain an average of 0.5 to 2kg during the first trimester, and 0.4 to 0.5kg per week during the second and third trimesters.
For women who were overweight before pregnancy (BMI 25-29.9), you should aim to gain an average of 0.5 to 2kg during the first trimester, and 0.2 to 0.3kg per week during the second and third trimesters.
Do keep in mind that you might not gain any weight during your first trimester as your baby will only grow to about pea-size.
Subscribe to receive newsletter on pregnancy and parenting in Singapore.