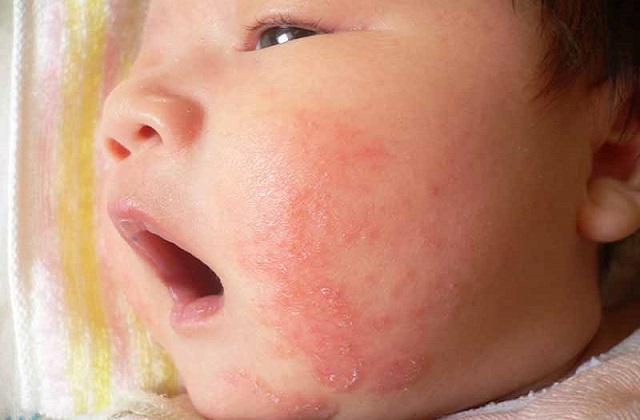
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a term for a group of medical conditions that cause skin to be inflamed or irritated. Eczema can make patches of skin to become rough or inflamed with blisters which may cause itching or even bleeding.
Types of Eczema
There are seven types of eczema. There are
1. Atopic dermatitis
2. Contact dermatitis
3. Dyshidrotic eczema
4. Hand eczema
5. Neurodermatitis
6. Nummular eczema
7.Stasis dermatitis
Out of these seven types of eczema, atopic dermatitis is the most common type.
Symptoms of Eczema
Some common symptoms of atopic dermatitis include the followings:
(a) Dry, scaly and itchy skin. Patches of chronically itchy, dry, thickened skin will usually appear on the scalp, cheeks, hands, elbows, neck, face, and legs.
(b) At the area infected, children may feel a burning sensation or pain.
(c) Other symptoms of eczema include red bumps that may ooze, drain, or crust.
Cause of Eczema or what trigger eczema
Until today, scientists still do not know the exact cause of eczema, but it is believed that hereditary and environmental factors are the one that contribute towards its occurrence.
Genetical factor
Children are more likely to develop eczema if his or her parent has had it or another atopic disease. If both his or her parents have an atopic disease, the chances increase further.
If a family member of the child has asthma or allergies, the child is also more likely to develop eczema.
Some studies also suggest that mother’s age at the birth of the child is also correlated to the occurrence of the eczema in children. These studies show that children born to older mothers are more likely to develop eczema than children born to younger mothers.
Environmental Factors
Environemtnal pollution
Studies have shown that it is more likely for children to develop eczema in area where there is more environmental pollution.
Soap and detergents
Soaps and detergents can remove the natural oils released from the skin. This however makes the skin dry and more sensitive to irritants.
Hot and cold temperature
It has been known that extremes of temperature and humidity may trigger a flare-up of eczema symptoms.
Other environmental factors that trigger the symptoms of eczema in children or make it worse include:
Irritants: soaps, detergents, shampoos, disinfectants, juices from fresh fruits, meats or vegetables
Allergens: dust mites, pets, pollens, mold, dandruff
Microbes: bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, viruses, certain fungi
Food: dairy products, eggs, nuts and seeds, soy products, wheat
How to treat eczema?
There is no overall cure for eczema. Treatment for the conditions can only help to heal the affected skin and prevent flaring of the symptoms.
Warm bath
Bathing is the most effective way to treat dry skin. Bathing gives skin the moisture that it needs.
Remember to apply moisturizer as soon as possible after bathing so as to "lock in" moisture
Moisturizer
When your child’s skin gets too dry, it can become irritated and cause eczema to flare. Wind, low humidity, cold temperatures, harsh soaps all can lead to dry skin.
Ointment is the best class of moisturizer. Ointment helps to fight eczema by hydrating the skin and preventing water loss.
Prescription medicine
Prescription topical medications include steroids and topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs). These medications are applied to the affected area of the skin which can help to ease redness, rash and itching.
These are a type of anti-inflammatory medication and should relieve the main symptoms of eczema, such as skin inflammation and itchiness
Antibiotics may be prescribed if doctor finds any sign of infection such as fungal and viral infections
Over the counter (OTC) medicine
Usually, these products are used for moisturizing the skin and some are used to help to relieve symptom like rash, redness and itch; and some are for gently cleaning skin to prevent infection.
Phototherapy
In phototherapy, a special machine is used to emit narrowband ultraviolet B (UVB) light onto the skin in order to help reduce itching and inflammation. This is turn increases vitamin D production and bacteria-fighting systems in the skin.
How to prevent eczema?
Measures that can be taken to prevent eczema include the following:
1. First and foremost, follow doctor’s instruction closely. Some pediatricians in Singapore, like the ones in KK Women and Children’s hospital will give patients an “action plan”, remember to follow the plan closely.
2. Parents can take action to reduce the level of house dust mites as this is because house dust mites can trigger eczema.
3. Avoid stuffed toys, pets and carpets in the home as these can trigger eczema.
4. Family members should avoid smoking as a polluted environment can also trigger eczema.
5. Using mild soap or non-soap cleanser when washing.
6. Help your child to avoid sweating or overheating as swear can also trigger eczema.
7. Note down any foods that may cause an outbreak and avoid those foods.
8. Cut fingernail frequently and remind your child to avoid scratching.
9. Wearing cotton and soft fabrics, avoiding rough, scratchy fibers and tight-fitting clothing
10. Using a humidifier in dry or cold weather